Threats to our hedgerows

Although the rates of direct hedge removal have been reduced, we are still seeing the loss of hedges through mismanagement. With many farmland species now marginalised to hedgerows, we take a look at the issues that are threatening them.
Neglect from under management
The last Countryside Survey in 2007 saw a 9% increase in the number of hedges that had been lost to under management over the previous decade. Hedgerows require management in order to stop them developing into a line of trees. Over half the UK’s ‘priority species’ mammals make significant use of hedgerows for food, nesting/roosting and travelling through the landscape. As hedgerows grow upwards into a line of trees, the low shrubby cover that’s needed by wildlife for shelter, food and as corridors for travelling along, is gradually lost. A line of trees also develops gaps over time as trees are lost. Once a hedgerow has become a line of trees, it’s very difficult to return it to a shrubby hedgerow structure, and it will have lost many of its wildlife credentials. It’s therefore essential to prevent this structural decline.
Inappropriate cutting from over management
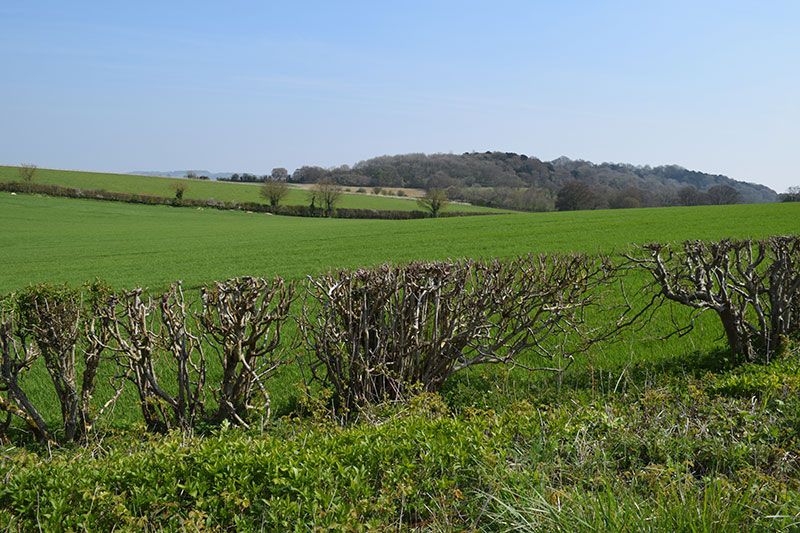
On the opposite end of the spectrum, over management can also threaten hedges. Cutting a hedge too often and at the same height, reduces the value of the hedge to wildlife and threatens the future of the hedge structure. Over management causes stem health to deteriorate which leads to gaps forming in the hedge. This impacts the hedge’s value as a wildlife corridor. Cutting hedges every year also significantly reduces the number of flowers and fruit available for wildlife to enjoy, as many of Britain’s native berry bearing species only flower on growth that is two years or older.
The timing of hedge cutting is also of huge importance to wildlife. 84% of Britain’s farmland birds for example, rely on hedgerows for food and protection. For over half of these, hedgerows are their primary habitat. No hedge should be cut in bird nesting season between March and the beginning of September. Ideally, trimming is left until January, so that hedgerow fruit/nuts are available to wildlife through the winter months.
Ploughing
Ploughing too near a hedge destroys the herbaceous vegetation that usually grows at the hedge base. It can also damage the roots of the shrubs and hedgerow trees that make up the hedge structure. If the root systems are no longer able to support them, this can sometimes kill the trees which leads to the loss of parts of the hedge. This is especially the case in times of drought.
Direct removal
Although the rates of direct removal have slowed in recent years, hedgerows can still be removed, with council permission, for agriculture or development. Any removal reduces how well connected the hedgerow network is for birds, bats, butterflies and other wildlife that use hedges as foraging and commuting habitats.
Spraying
Over 500 native plant species have been recorded as being supported by hedgerows. Herbicides sprayed too close to a hedge or in windy conditions, can kill off plant diversity, especially at the base. Similarly, fertilizers can cause a change in the type of plants growing at the hedge base. Many wildflowers do not thrive in enriched soils. This is because enrichment causes the rapid growth of nutrient-loving plants such as nettles and docks, which then dominate the ground vegetation.
Over 1,500 different insect species have been found feeding on or living in hedgerows. Pesticides can cause a decline in the number and diversity of these insects. This can have a knock-on effect on the wildlife that they feed, such as birds, bats and other mammals.
Health-check your hedgerows
The Healthy Hedgerows survey provides instant feedback about the health of the hedge and bespoke management advice. The data that you contribute helps us to understand the overall health of hedgerows at a national scale so that we are able to direct our conservation work. Learn more:

